
BMI, or Body Mass Index, is a widely used measure to assess an individual's body weight in relation to their height. It provides a simple way to categorize a person's weight into various classes, from underweight to obese, helping to identify potential health risks associated with weight.
BMI is calculated using a person's weight (in kilograms) and height (in meters) with the following formula:
BMI = weight (kg) / (height (m) * height (m))
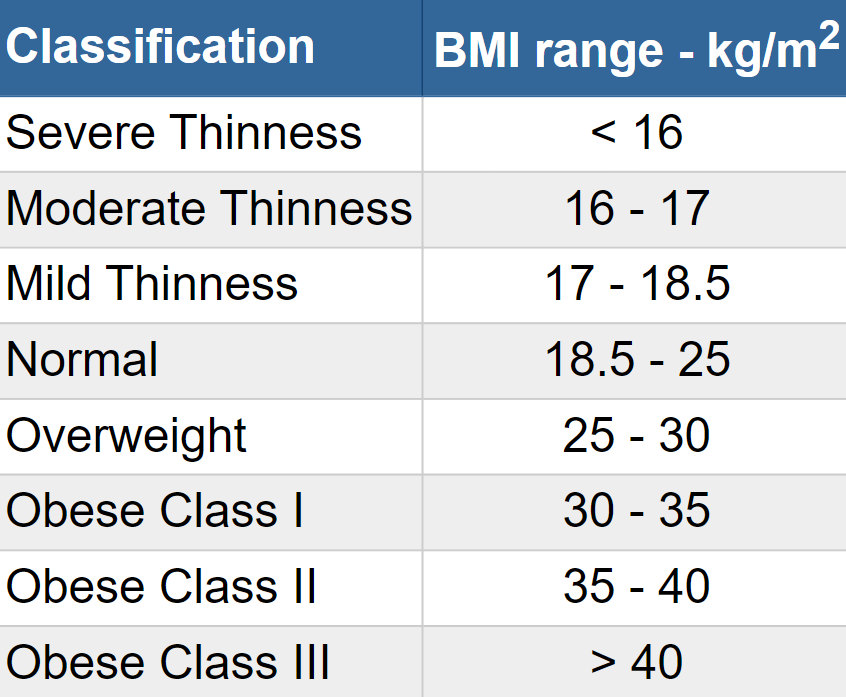
The result is a numerical value that falls into one of the following categories:
Underweight: BMI < 18.5
Normal weight: 18.5 <= BMI < 24.9
Overweight: 25 <= BMI < 29.9
Obese: BMI >= 30
Please note that while BMI can be a useful tool, it has its limitations. It doesn't take into account factors like muscle mass, bone density, and distribution of fat. Therefore, it's essential to interpret BMI results in conjunction with other health assessments.
Use our BMI calculator below to find out your BMI. Simply enter your weight in kilograms and your height in meters, and the calculator will give you your BMI category.
This is the World Health Organization's (WHO) recommended body weight based on BMI values for adults. It is used for both men and women, age 20 or older.
At EmbracingHonesty, we understand that an individual's Body Mass Index (BMI) is not just a number on a scale; it can have broader implications for mental health and overall well-being. While BMI primarily measures physical health, its influence on mental health can be observed through several interconnected aspects:
MI plays a role in shaping how we perceive our bodies, which, in turn, affects self-esteem. This self-perception can have significant implications for mental health, with low or high BMIs potentially contributing to body image concerns and related mental health challenges.
Emotional eating, triggered by stress, anxiety, or depression, can impact BMI. When individuals use food as a way to cope with their emotions, it can lead to weight fluctuations and associated mental health concerns.
Weight-based stigma and discrimination, often faced by individuals with higher BMIs, can result in mental health issues like low self-esteem, social isolation, and a negative impact on overall well-being and also mental health challenges such as depression, anxiety, or even eating disorders.
